Week #16
11 Feb 20191. Subjects shuffling results
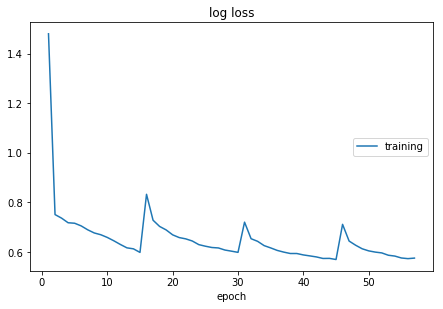
Observing that the loss doesn’t decrease smoothly using 2 objects shuffling and 3 objects shuffling, so the 330 total subject shuffling is performed. It takes 30 minutes to do one epoch over all subject, so doing 500 epochs, it takes about 10 days for training.
2. Existed Parcellation scales
2.1 Challenges
This website concludes an overview of all challenges that have been organized within the area of medical image analysis. Filterd with “MRI Brain Segmentation”, we get 20 challenges in the past years. The table below is a summary of the challenges.
| Challenge | Labels | Sub’ num | Health Condition | Link |
| MRBrainS18 | 8/3 | 30 | patients with diabetes, dementia and Alzheimers, and matched controls (with increased cardiovascular risk) with varying degrees of atrophy and white matter lesions (age > 50) | Link |
| BRATS 2018 | 3 tumor labels | 274 MRI scans(2015) for training, 110 scans for testing | Link | |
| WMH Segmentation Challenge | white matter hyperintensitie | training:60 scans, testing:110 scans,T1 and FLAIR | N.A | Link |
| iSeg-2017 | white matter (WM), gray matter (GM), and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) | T1 and T2 weighted | 6-month infant brain | Link |
| ISLES | stroke lesions | 43 training subjects, 43 stroke case for testing | stroke patients | Link |
| ENIGMA cerebellum | Link |
3. How to define Loss Function having multiple resolution
In [1],they co-reistered each subject’s image volumes rigidly to the T1c MRI, which had the highest spatial resolution in most cases, and resampled all images to 1mm isotropic resolution in a standardized axial orientation with a linear interpolator. They used a rigid registration model with mutual information similarity metric as it is implemented in ITK [2], (“VersorRigid3DTransform” with “MattesMutualInforma- tion” similarity metric and three multi-resolution levels)
Paper Review
Zhuang, Juntang. “LadderNet: Multi-Path Networks Based on U-Net for Medical Image Segmentation.” ArXiv:1810.07810 [Cs, Eess], Oct. 2018. arXiv.org. Link
- LadderNet: a chain of multiple U-Net, it has multiple pairs of encoder-decoder branches, and has skip connections between every pair of adjacent decoder and decoder branches in each level.
Alom, Zahangir, et al. Recurrent Residual Convolutional Neural Network Based on U-Net (R2U-Net) for Medical Image Segmentation. p. 12.Link
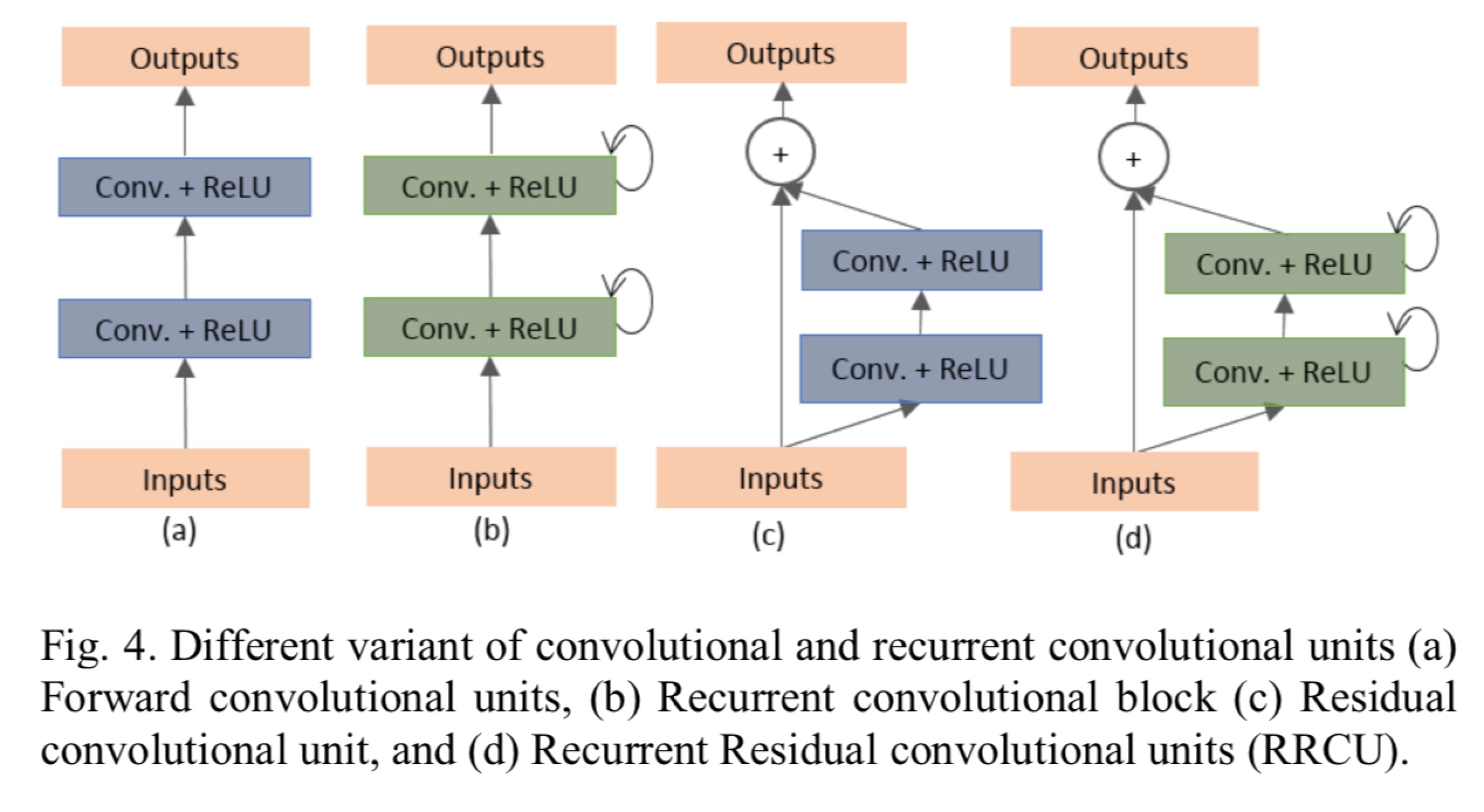
- Recurrent convolutional neural network (RCNN) based on U-Net (RU-Net) as well as a Recurrent Residual Convolutional Neural Network based on U-Net (R2U-Net) models. The Proposed deep learning models are the building blocks of the stacked convolutional units shown in Fig. 4(b) and (d).
- Database:
- blood vessel segmentation in retina image
- skin cancer segmentation
- lung lesion segmentation
- Same number of network parameters with better performance against U-net.
- Retina blood vessel segmentation:
- DRIVE: 40 color images. 20 for training, 20 for testing. original image size is 565 x 584, cropped to 565 x 565. 190,000 randomly selected patches (48x48) 171,000 for training, 19,000 for validation.
- STARE: 20 color images. original image size 700x605. Training is performed with randomly selected samples from all 20 images. Using ‘leave-one-out’ strategy where 19 randomly selected samples are used for training, 1 for test. 250,000 patches where 225,000 for training, 25,000 for validation.
- CHASH_DB1: 28 color images, size 999 x 960. 20 samples for training and 8 samples for testing.
- Skin Cancer segmentation: (Adam optimization)
- 2000 samples in total. 1250 training, 150 validation and 600 testing. Original size: 700x900, rescaled to 256x256.
- Lung Segmentation:
- 534 2D samples, 70% are used for training and 30% are used for testing. Original image size is 512 x 512, resized to 256x256.
References
[1] B. H. Menze et al., “The Multimodal Brain Tumor Image Segmentation Benchmark (BRATS),” IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, vol. 34, no. 10, pp. 1993–2024, Oct. 2015. [2] L. Ibanez et al., The ITK Software Guide. Clifton Park, NY: Kitware, 2003.